1. H-1B visa
GS Paper II: IR -Bilateral relations, diaspora issues, economic diplomacy
Context: Presidential order introduced a $100,000 fee for new H-1B requests.Objective is to address program abuses and prioritize U.S. workers.
- Recent USCIS guidance (Oct 2025) clarified exemptions, providing relief to existing holders.
What is an H-1B Visa?
- Nonimmigrant work visa for specialty occupations requiring bachelor’s degree.
- Enables U.S. employers to hire skilled foreign workers in fields like IT, engineering, medicine.
- Issued for 3 years initially, extendable to 6 years, may lead to residency.
- Annual cap: 85,000 visas, including 20,000 for advanced U.S. degree holders.
What’s the News in 2025?
- Proclamation imposes one-time $100,000 fee after Sep 21, 2025, for new applications filed abroad.
- Fee aims to deter program abuse, fund U.S. workforce training.
- Companies pause H-1B hiring, legal challenges emerge.
USCIS Clarification (Oct 2025)
- $100,000 fee does not apply to change of status, extensions, amendments for those already in U.S..
- Applies only to new consular/port-of-entry petitions from outside U.S..
- Exemptions: universities, nonprofits, healthcare, national interest cases.
Why the Controversy?
- High fee seen as unaffordable, impacting startups, universities, small firms.
- Critics say it restricts skilled global talent and U.S. competitiveness.
- Viewed as anti-immigrant, possibly pushing jobs offshore.
- Legal challenges argue it oversteps executive powers.
Indian Connection
- Indians get about 70% of all H-1B visas annually.
- Major Indian IT firms (TCS, Infosys, Wipro) rely on H-1B, but dependence is falling.
- Many Indian students shift from F-1 to H-1B status.
- Policy created panic among Indian professionals, impacting migration plans.
Why is it Significant for India?
- a) Economic Impact
- Changes could reduce $5 billion in remittances, but may boost Indian IT’s domestic operations.
- IT export revenues, innovation links with U.S. could be affected.
- Small startups face barriers to U.S. expansion.
b) Employment Impact
- Over 500,000 Indians on H-1B: limits future migration, may create reverse brain drain.
- Could benefit local job market, but disrupt careers and families.
- Clarifications offer stability for current Indian workers.
- c) Diplomatic Angle
- May strain U.S.-India ties, with humanitarian and strategic concerns.
- Immigration debates could affect broader trade and partnership talks.
- India may push policy reforms to retain/attract top talent.
Conclusion: The 2025 H-1B visa fee marks a major U.S. immigration shift, aiming for protectionism but balanced with talent needs.
- Exemptions provide relief to current holders, but challenge India’s future tech talent flows.
- Long-term, it could accelerate India’s domestic growth, requiring continued diversification of global opportunities.
2. India must counter chinas plaint at WTO on Ev car shop,battery PLI plan
GS Paper II (Governance, International Relations)
GS Paper III (Economics, Indian Economy, Industry, WTO and Trade Policy)
Context: China filed a complaint at the WTO against India’s Production Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes for EVs, advanced batteries, and automobiles, alleging they discriminate against foreign, especially Chinese, products.
Background – About the Schemes
| Scheme | Aim | Key Features |
| a) PLI for ACC Batteries | Boost domestic giga-scale advanced battery manufacturing | ₹18,100 crore outlay, phased domestic value-addition, 50 GWh target, local supply chain development |
| b) PLI Auto Scheme | Promote advanced automotive tech & cut imports | ₹25,938 crore outlay, tech-focused, job creation, incentivizes domestic production |
| c) EV Passenger Car Scheme (2024–25) | Support EV manufacturing and adoption | Linked to local value-addition, supports OEMs, nurtures EV ecosystem |
China’s Complaint at WTO – Key Failures Alleged
Allegations
- (1) Violation of WTO Subsidies & Countervailing Measures (SCM) Agreement – schemes based on domestic content for incentives.
- (2) Violation of National Treatment (GATT Article III) – foreign goods face a disadvantage in market access.
- (3) Indirect discrimination against Chinese-origin goods by preferring local inputs.
India’s Stand and Strategy
- India argues PLI is for tech development, not anti-foreign discrimination; aims to reduce import dependence and boost manufacturing.
- Developing economies need policy space for industry nurturing, especially in emerging tech sectors.
- Domestic incentive policies are a global grey area; India may cite precedents of similar support by China/EU.
Broader WTO Role – Steps & Explanation
| Step | Explanation |
| 1. Consultations | Initial talks (60 days) to resolve dispute bilaterally |
| 2. Panel | If talks fail, panel set up to adjudicate; can take 6–9 months |
| 3. Appeal | Any party can appeal panel ruling; current appellate system hampered/disputed |
Why This Matters
Economic Significance
- Protects India’s nascent EV, battery, and auto sectors and aims to build global champions.
- Local value-addition boosts jobs, skill development, and domestic supply chains.
Geopolitical Angle
- Demonstrates rising trade frictions with China amid tech and economic rivalry.
- Asserts India’s right to support sunrise industries against established global dominance (esp. China in batteries/EVs).
Trade Policy Angle
- Testing ground for WTO’s effectiveness on new-gen industrial incentives and fair competition.
- Shapes future use of PLI-type developmental state policies for other tech sectors.
Conclusion
- The WTO dispute is a landmark for India’s industrial policy; balancing development needs and global trade rules will be crucial.
- Outcome will influence not just EVs and batteries, but the global legitimacy of state-led tech promotion.
3. Net FDI inflow fell by 159% in August :RBI’s date reveals
GS Paper III: Economic development, external sector challenges, RBI policies
Why in News – What Happened?
- RBI’s October 21, 2025 bulletin showed India’s net FDI in August turned negative, with outflows exceeding inflows by $616 million.
- Marked second negative FDI month in FY26, driven by repatriation by foreign firms and increased Indian investments abroad.
- Coincides with core sector slowdown to 3% growth in September 2025, highlighting broader caution.
What is FDI?
- Foreign Direct Investment means overseas entities invest in Indian businesses/assets, aiming for lasting influence and management control.
- Involves new factories, offices, acquisitions, and transfers of capital, technology, and jobs.
- Key driver for India’s growth and global integration.
What is Net FDI?
- Net FDI equals gross FDI inflows minus outward FDI and repatriations/disinvestment by foreign companies.
- A positive net signals capital expansion; negative means more capital leaves than enters, which may affect forex and investment climate.
- Central banks use it to gauge investor confidence.
Data Summary (August 2025)
| Component | Amount (USD mn) | Change YoY (%) | Change MoM (%) |
| Gross Inward FDI | 6,049 | -30.6 | -45.5 |
| Repatriation/Disinvestment | 4,928 | -5.4 | +30.0 |
| Outward FDI | 1,736 | -29.7 | Not Specified |
| Net FDI | -616 | -159.0 | Positive → Negative (July: +5,000) |
- Drop in gross inflows and jump in repatriation caused the negative monthly balance.
- Gross inflows and outward FDI both fell, but outflows outpaced inflows.
Interpretation – Short Term (August)
- Negative net FDI reflects volatility, with investor caution amid global and domestic uncertainty.
- RBI had to sell $7.7 billion to stabilize rupee, showing pressure on FX reserves.
- Contrasts July’s positive net; suggests uneven recovery after shocks.
Why Did It Happen?
- Gross inflows plunged due to global uncertainties, US trade actions, and sectoral slowdowns.
- Foreign firms repatriated profits aggressively amid equity outflows and weak rupee.
- Outward FDI contracted but couldn’t offset high repatriations.
Significance for India’s Economy
Economic Growth
- Long-term net FDI (Apr-Aug) still rose 121% YoY, showing overall investor confidence.
- However, monthly volatility may slow job creation/tech transfer in short run.
Balance of Payments
- Strong cumulative inflows support long-term forex reserves.
- Outflows, FPI selling ($2.5 billion Apr-Aug), pressure rupee and could raise inflation risks.
Policy Implications
- Outward FDI shows Indian firms’ global expansion and economic maturity.
- Negative net may prompt policy tweaks, like liberal FDI norms, needed to reverse short-term declines.
4. Microbial Link Between Arsenic in Soil and Lower Rice Yield Uncovered
Context :A recent scientific study has shown that the type of microbial community present in rice paddy soils plays a critical role in determining arsenic buildup in rice grains, raising significant food safety concerns.
Arsenic Toxicity in Agriculture
- Arsenic is a potent carcinogen and plant toxin, accumulating in rice and posing severe health and crop risks, especially in Asia.
- In flooded, oxygen-poor fields, soil microbes convert arsenic into soluble, bioavailable forms, easily absorbed by rice roots.
- Toxic species like dimethylarsinic acid (DMA) and dimethylated monothioarsenate (DMMTA) cause “straighthead disease,” leading to crop sterility and yield losses.
- Arsenic toxicity in rice depends on the chemical form (speciation) rather than just total soil concentrations, so even low-arsenic soils can be dangerous.
- Hotspots include regions like West Bengal, Bihar, and Bangladesh where irrigation relies on arsenic-laden groundwater.
Soil Age and Microbial Composition
- A recent study by Peng Wang and team found that soil age influences which microbes dominate and how they manage arsenic.
- Young paddy soils (<700 years) have more arsenic-methylating bacteria, producing toxic organic forms.
- Older soils (>700 years) contain more demethylating archaea, which break down and detoxify these compounds.
- A global analysis across 801 paddy soils identified 11 key methylators and 6 demethylators as central to toxicity outcomes.
- When the ratio of methylators to demethylators exceeds 1.5, the risk of toxic arsenic build-up and straighthead disease increases sharply.
How Microbial Balance Governs Arsenic Toxicity
- Arsenic toxicity in rice fields is controlled by the balance between methylating bacteria (risk-raisers) and demethylating archaea (detoxifiers).
- Environmental factors like flood timing, oxygen, temperature, and water management can shift this balance, sometimes increasing toxicity.
- Solutions include practices like mid-season drainage, silicon fertilization, and targeted microbial management to reduce arsenic uptake in rice.
5. FATF may dicuss state sponsorship of terrorism;PAKISTAN entities in focus
GS Paper II: International Relations , Topic: India-Pakistan Relations & Global Security
Context: FATF meetings in Paris set to deliberate state sponsorship of terrorism, focusing on Pakistan-backed outfits and proxies.
- Over 130 terror entities linked to Pakistan feature on UN sanctions lists, including recent attacks like in Pahalgam condemned globally.
Why it Matters for India ?
- Direct links between state sponsorship and cross-border terrorism threaten India’s security and stability.
- Terror funds and support from Pakistan impact internal peace and counter-terror operations, especially in J&K.
About FATF – Key Aspects
| Aspect | Details |
| Mandate | Intergovernmental watchdog to combat money laundering & terror financing |
| Member Countries | Over 200 jurisdictions and observers |
| Black/Grey List | Monitors nations enabling illicit funds and terrorism |
| Plenary Meetings | Held periodically to discuss new risks & actions |
Details – What’s New This Time?
- FATF to officially discuss state-sponsored terror financing as a long-standing global risk; focus includes Pakistan’s role.
- LeT/JuD’s reconstruction funds, rooted in alleged state and charitable “relief” money, under international scrutiny.
Pakistan Under the Lens
- Pakistani government accused of financing banned groups under humanitarian pretexts (e.g., “relief for flood victims”).
- FATF will review recent allocations to LeT for infrastructure rebuilding after Indian Air Force action.
Key Facts Highlighted
- U.S. and UN lists designate over 130 Pakistan-linked entities as global terror threats.
- May 2025: Pakistan announced public funding for LeT and Jaish-e-Mohammad facilities rebuild.
- Security agencies flagged diversion of “relief” funds to terrorist causes.
FATF Previous Statements
- June: FATF condemned Pahalgam killings, stressed that terror attacks need state support and money flows.
- July: FATF called state sponsorship a persistent threat to peace/security, marking its first official recognition in key reports.
Border Context – Pakistan & FATF
- India faces recurrent cross-border attacks linked to FATF-listed entities.
- FATF scrutiny increases accountability pressure on Pakistan amid ongoing tensions and terror incidents
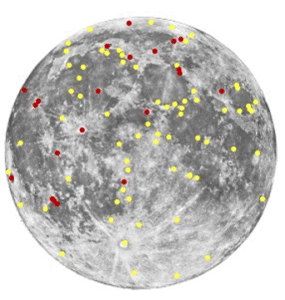
6. Transient Lunar Phenomena
GS paper I: Geography Important Geophysical Phenomena
Context: Recent scientific investigations have brought renewed attention to mysterious, short-lived light events on the Moon’s surface, known as Transient Lunar Phenomena (TLPs).
What are Transient Lunar Phenomena?
- Brief flashes, glows, or hazy regions visible on the Moon, lasting from seconds to hours before fading.
- Over centuries, thousands of such events have been recorded, including during Apollo 11.
Types and Regions of Occurrence
- TLPs include reddish glows, star-like bursts, and mist-like patches.
- Most frequently observed near the Aristarchus and Plato craters, considered highly dynamic lunar zones.
Scientific Importance
- These phenomena suggest ongoing geological or surface activities, challenging older notions of a dormant Moon.
- Studying TLPs helps reveal current surface dynamics and possible internal moon processes.
Proposed Origins of TLPs
- Lunar Outgassing: Escape of gases like radon or argon through fissures, producing luminous effects.
- Meteoroid Impacts: Frequent impacts by space rocks causing brief, visible flashes.
- Electrostatic Dust: Solar radiation charges dust, leading to levitation and light scattering.
- Atmospheric Artifacts: Some phenomena may result from Earth’s atmospheric distortion during observations.
Latest Research & Observing Efforts
- Automated telescopes and CCD imaging systems enable real-time detection of TLPs.
- Space missions (NASA’s LRO, ISRO’s Chandrayaan) monitor lunar surface gas emissions and new impact events.
- Spectroscopic studies support lunar outgassing, especially in Aristarchus.
- Global monitoring integrates optical, seismic, and spectral data for confirmation.
Scientific Objective
- To better understand lunar geology, monitor surface changes, and confirm that the Moon is still an active body