1.LVM3 M6 Mission
GS Paper III-Science and technology
Context :ISRO’s upcoming LVM3 M6 launch on 24 December will place the BlueBird Block‑2 satellite in orbit.
- The launch is under a commercial agreement with U.S.–based company AST SpaceMobile.
- The satellite will provide high‑speed cellular broadband directly to smartphones globally.
What is Low Earth Orbit (LEO)?
- Region of space close to Earth, typically from about km to km altitude.
- Satellites in LEO have short orbital periods (around 90–120 minutes per revolution).
- LEO allows lower latency and stronger signals, useful for communication and Earth‑observation satellites.
What is BlueBird Block‑2 satellite?
- A large, next‑generation commercial communication satellite of AST SpaceMobile.
- Designed to deliver space‑based 4G/5G broadband directly to standard mobile phones.
- Will operate in low Earth orbit as part of a larger constellation for global coverage.
- Described as the largest commercial communication satellite to be deployed in LEO.
About AST SpaceMobile
- A U.S.–based company building a space‑based cellular broadband network.
- Aims to provide direct‑to‑device connectivity for both commercial and government users.
- Its goal is to bridge connectivity gaps for billions of mobile users worldwide.
Existing AST SpaceMobile network
- Has launched five satellites, BlueBird 1–5, as of September 2024.
- These satellites enable continuous Internet coverage across the U.S. and some other countries.
- Operates through partnerships with over 50 mobile network operators globally.
Future plans of AST SpaceMobile
- Plans to launch more BlueBird‑series satellites to expand global coverage.
- Intends to build a full constellation for near‑continuous direct‑to‑phone broadband.
- Will continue collaborating with mobile operators for commercial rollout in more regions.
Why is BlueBird Block‑2 important?
- Key step in scaling AST’s constellation from test phase to higher‑capacity operations.
- Supports “direct‑to‑smartphone” broadband without needing special satellite phones.
- Enhances India’s commercial launch profile through ISRO’s LVM3 heavy‑lift vehicle.
- Contributes to bridging rural and remote connectivity gaps worldwide.
- Strengthens India’s role in the emerging global satellite‑based mobile broadband market.
2. Will new act aid indias nuclear development ?
GS paper III-Science and technology
Context :Parliament has enacted the Sustainable Harnessing and Advancement of Nuclear Energy for Transforming India (SHANTI) Act, reshaping the legal framework for India’s civilian nuclear programme.
The story so far
- SHANTI Act replaces the Atomic Energy Act, 1962 and the Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage (CLND) Act, 2010.
- It aims to accelerate nuclear power expansion and attract greater private and foreign participation.
Why is SHANTI significant?
- It allows private companies to build and operate nuclear plants, with scope for foreign investment.
- India targets raising nuclear capacity from 8.8 GW to 100 GW by 2047, with major additions from state and private players.
What are the major differences in SHANTI?
- Earlier operator‑only liability is replaced by provisions that can involve suppliers for compensation in defined cases.
- The Act streamlines nuclear material control and relaxes some older technology‑transfer constraints under global agreements.
Does SHANTI load the dice against operators?
- SHANTI introduces graded liability caps depending on plant size and capacity.
- Compensation must match damage level, but operators can avoid liability if supplier fault is legally established.
Will SHANTI spur India’s nuclear vision?
- The Act is meant to de‑risk private investors and align with India’s goal of low‑carbon baseload power.
- Challenges remain over safety perceptions, high project costs and timely development of Small Modular Reactors
3. VB-G RAM G Bill
GS II-polity
Context :President Droupadi Murmu granted assent to VB-G RAM G Bill on Dec 21, 2025, replacing MGNREGA.
- Parliament passed the bill amid strong Congress-led protests.
Origins of MGNREGA
- Enacted in 2005 as NREGA by UPA government.
- Renamed MGNREGA in 2009 to honor Mahatma Gandhi.
- Inspired by right-to-work under Article 21; evolved from earlier rural schemes like JRY.
Bill Passage and Parliamentary Corruption
- Passed in Lok Sabha (Dec 16) and Rajya Sabha (Dec 18) amid opposition walkouts.
- Congress alleged bulldozing without debate; called it dismantling of rights-based law.
Why MGNREGA is Unique
- Legal guarantee of 100 days unskilled work per rural household.
- Demand-driven: Work on application within 15 days; unemployment allowance if delayed.
- Decentralized: Gram Sabha plans works; social audits ensure transparency.
- Focus on asset creation (e.g., water conservation) and women empowerment.
Government Rationale for Replacement
- Aligns with Viksit Bharat @2047 vision for modern rural development.
- MGNREGA outdated; rural economy transformed with higher incomes.
- Addresses issues like poor asset quality, corruption, and labor shortages in agriculture.
How VB-G RAM G Bill Differs from MGNREGA
- Increases guarantee to 125 days (from 100).
- 60:40 Centre-State fund sharing (MGNREGA: Centre bore full wages).
- Supply-driven with budget caps; focuses on 4 areas: water security, rural infrastructure, livelihoods, weather mitigation.
- Works from Viksit Gram Panchayat Plans; integrates with PM Gati Shakti.
- Allows 60-day pause during peak agricultural seasons.
4. ICGS Amulya.
GS paper III-science and technology
Context :Recently commissioned into Indian Coast Guard service at Goa as ICGS Amulya.
- Enhances coastal security, anti‑smuggling and search‑and‑rescue capacity on the eastern seaboard.

What is ICGS Amulya?
- Third ship of the Adamya‑class Fast Patrol Vessels for the Indian Coast Guard.
- Designed for rapid‑response and extended maritime patrols in India’s EEZ and coastal waters.
Designer, builder and indigenisation
- Designed and built by Goa Shipyard Limited, a defence public sector shipyard.
- Uses more than 60% indigenous components, aligning with Make‑in‑India and Atmanirbhar Bharat.
Key technical features
- 51‑metre-long fast patrol vessel optimised for coastal and offshore missions.
- Powered by two advanced 3000 kW diesel engines driving high‑performance propulsion.
- Maximum speed of around 27 knots for quick interception of hostile or suspicious vessels.
- Endurance of about 1,500 nautical miles, allowing multi‑day patrols without refuelling.
- Fitted with indigenous state‑of‑the‑art weapons, sensors and communication systems.
Operational roles
- Maritime surveillance and patrol to enforce law and order at sea.
- Interdiction of suspicious craft involved in smuggling, piracy or illegal fishing.
- Search and Rescue operations for distressed fishermen and merchant shipping.
- Pollution response and support in containing oil spills or marine environmental incidents.
Deployment
- To be based at Paradip, Odisha, under Coast Guard Region (North East).
- Will strengthen security along India’s eastern coast and approaches to the Bay of Bengal.
5. Where does India stand on child marriage?
GS Paper III: Inclusive Growth, Social Sector Initiatives
Context :Bal Vivah Mukta Bharat Abhiyan Launch _Union government launched 100-day awareness campaign in December 2025.
-
- Part of India’s commitment to end child marriage by 2030 (UN SDG Target 5.3).
- First anniversary of campaign celebrated recently.
India’s Progress on Child Marriage
- Significant Decline
- From 47.4% (2005-06) to 26.8% (2015-16) and 23.3% (2019-21) among women aged 20-24.
- Halved since Prohibition of Child Marriage Act, 2006.
- Regional & Socio-Economic Disparities
- Highest: West Bengal (40%), Tripura (42%), Bihar.
- Lowest: Lakshadweep (4%), J&K, Ladakh, HP, Goa (6-7%).
- 48% girls with no education vs 4% with higher education married before 18.
Key Schemes & Interventions
- Bal Vivah Mukta Bharat Abhiyan
- 54,917 child marriage prevention officers appointed.
- 1,520 instances prevented through persuasion/administrative action.
- Beti Bachao Beti Padhao
- Focuses on girl child education, empowerment, and sex ratio improvement.
- Other Measures
- Ladli schemes provide financial support for girl child.
- Initiatives for school enrolment, safe transport, sanitation.
Challenges & Legal Aspects
- Slow Progress
- Only 3.5% decline in last five years.
- Needs 20x faster pace to meet 2030 SDG target.
- Proposed Legal Change
- Government bill to raise women’s marriage age to 21.
- Opposed; 61% women aged 20-24 already married before 21.
Conclusion Child marriage remains in news due to renewed government campaign, slow progress towards SDG 2030 target, and ongoing debate on raising legal marriage age.
6. India -Africa Economic ties
GS paper II-IR
CONTEXT :PM Modi’s visits to Namibia, Ghana (July 2025) and Ethiopia highlight India-Africa ties.
Why India-Africa Relations Focused
- Rising Western market uncertainties push India to diversify.
- Africa offers growing markets, critical minerals, and strategic partnerships.
- PM Modi’s 2025 Africa visits boost Global South outreach.
Why Africa Matters More to India Today
- Provides critical minerals for green transition and manufacturing.
- Large young population and markets for Indian goods/services.
- Counterbalance to China’s dominance in Africa.
Current Status of India-Africa Trade
- Bilateral trade crossed $100 billion in FY 2024-25.
- India’s exports: ~$38-42 billion (petroleum, pharma, rice, engineering goods).
- Key partners: Nigeria, South Africa, Tanzania.
Comparison with China-India (India vs China in Africa Trade)
| Indicator | India | China |
| Bilateral trade (2024) | ~$100 billion | ~$295-296 billion |
| India’s rank in Africa | 3rd-4th largest partner | Largest partner |
| Africa’s imports share | ~6% from India | ~21% from China |
| Key exports to Africa | Pharma, rice, textiles | Machinery, electronics |
| Investments (cumulative) | >$75 billion | Much higher (infrastructure focus) |
India Targets & Need for Strategy
- Target: Double trade with Africa by 2030 (to ~$164-200 billion).
- Need: Counter US/EU market risks; secure minerals; leverage AfCFTA.
Five Strategic Pillars for India-Africa Economic Engagements
- Negotiate preferential trade agreements with AfCFTA and regional blocs.
- Shift to joint ventures and manufacturing units in Africa.
- Scale up trade finance and Lines of Credit for MSMEs.
- Invest in ports, logistics, and maritime corridors.
- Boost services, digital trade, IT, health, and skill development.
Role of Indian Public Sector & Investment
- Lead in mining, minerals, infrastructure, and renewable energy.
- Strengthen investments to overcome hurdles like bureaucracy.
- Public sector units drive long-term sustainable partnerships.
Broader Strategic Significance
- Secures resources for India’s growth and energy needs.
- Enhances India’s influence in multipolar world.
- Builds sustainable ties beyond transactional trade.
7. UN Peacekeeping
General Studies Paper‑II -IR
Context :recent drone attack on a UN logistics base in Kadugli, South Kordofan (Sudan) killed six Bangladeshi peacekeepers of UNISFA and injured several others, prompting a strong condemnation by the UN Security Council for targeting UN personnel and violating international humanitarian law. 
UN Peacekeeping: basic idea
- UN peacekeeping helps conflict‑affected states move from war to peace by stabilising situations and backing political processes.
- Missions combine military, police and civilian components under UN command and Security Council mandates.
Evolution of UN peacekeeping
- 1948 beginnings: Started with unarmed observer missions such as UNTSO to monitor ceasefires and report violations.
- Cold War phase: Geopolitical rivalry kept mandates narrow, focusing on consent‑based monitoring with limited enforcement.
- Post‑1990s expansion: Civil wars led to multidimensional missions including protection, mediation and institution‑building.
- Brahimi reforms (2000): Recommended clear mandates, better resources, quick deployment and priority to civilian protection.
Core tasks of UN peacekeepers
- Monitor ceasefires and buffer zones to prevent resumption of fighting.
- Protect civilians under imminent threat, including limited use of force when authorised.
- Support DDR programmes to disarm ex‑combatants and help their return to civilian life.
- Assist in elections, governance support and strengthening state institutions.
- Promote human rights and rule of law through monitoring and justice‑sector support.
- Facilitate humanitarian aid and early recovery in post‑conflict environments.
India’s role in UN peacekeeping
- Major contributor: India is among the largest suppliers of uniformed personnel to UN operations.
- Scale of service: Over 2.9 lakh Indian peacekeepers have participated in more than fifty missions worldwide.
- Current presence: Roughly 5,000 Indian troops and police are deployed in about nine ongoing missions.
- Sacrifice: Nearly 180 Indian peacekeepers have laid down their lives serving under the UN flag, reflecting India’s long‑standing commitment.
8. Arctic region
GS PAPER I-Geography -mapping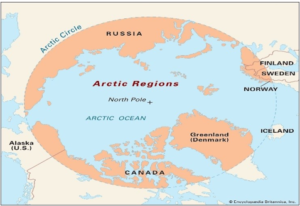
Context : recent NOAA assessment found that it has just recorded its warmest and wettest year ever, with temperatures rising at more than twice the global average and sea‑ice shrinking sharply.
Arctic: basic overview
- Earth’s northern polar zone marked by severe cold, sea ice, permafrost and specialised ecosystems.
- Crucial for global climate regulation because its bright ice strongly reflects incoming solar radiation.
Location and extent
- Lies mainly north of the Arctic Circle, around latitude 66.5° N.
- Geographically centred on the Arctic Ocean and its surrounding landmasses.
Countries with Arctic territory
- Region includes portions of Russia, Canada and the United States (Alaska).
- Also covers areas of Denmark (Greenland), Norway, Sweden, Finland and Iceland.
Major rivers flowing into Arctic Ocean
- From Russia: Ob, Yenisei and Lena carry large freshwater and sediment loads.
- From North America: Mackenzie in Canada and the Yukon flowing through USA–Canada.
Key physical and geological traits
- Arctic Ocean is the smallest, shallowest and one of the coldest of the world’s oceans.
- Wide continental shelves contain significant hydrocarbon, mineral and fishing resources.
- Lomonosov Ridge is a submarine mountain chain at the centre of overlapping seabed claims.
- Permafrost under land and seabed locks in huge stores of carbon and methane.
Notable characteristics
- Roughly one‑fifth of global freshwater is stored here in ice sheets, glaciers and snowpacks.
- Sea‑ice cover reflects about four‑fifths of incoming sunlight, acting as a planetary “cooler.”
- Experiences long polar night in winter and continuous daylight (midnight sun) in summer.
- Rapid warming and permafrost thaw are causing effects like “rust‑coloured” rivers from released metals.

